Rhinestone Protocol
Rhinestone is building at the frontier of modular account abstraction. We imagine a world where smart accounts become vanilla kernels and all the interesting features and components move to the module layer. However, for the module ecosystem to be permissionless, open, and interoperable across any smart account, several challenges need resolving.
- Security: Developers and end users require assurances that a third-party module is not malicious.
- Developer complexity: The complexities of modular smart accounts need to be abstracted from the developer.
- Interoperability: We still require a translation layer between different account implementations so that module developers need only build once for maximum distribution.
- Accessibility: Installing and using a module at the application layer should be as simple as installing an app.
Protocol Architecture
The Rhinestone Protocol consists of several key components that facilitate the lifecycle of smart account modules from development through to account installation and monetization. The protocol is account implementation agnostic, with the primary objective of being a credibly neutral middleware layer that solves user security, account portability, and account extensibility.
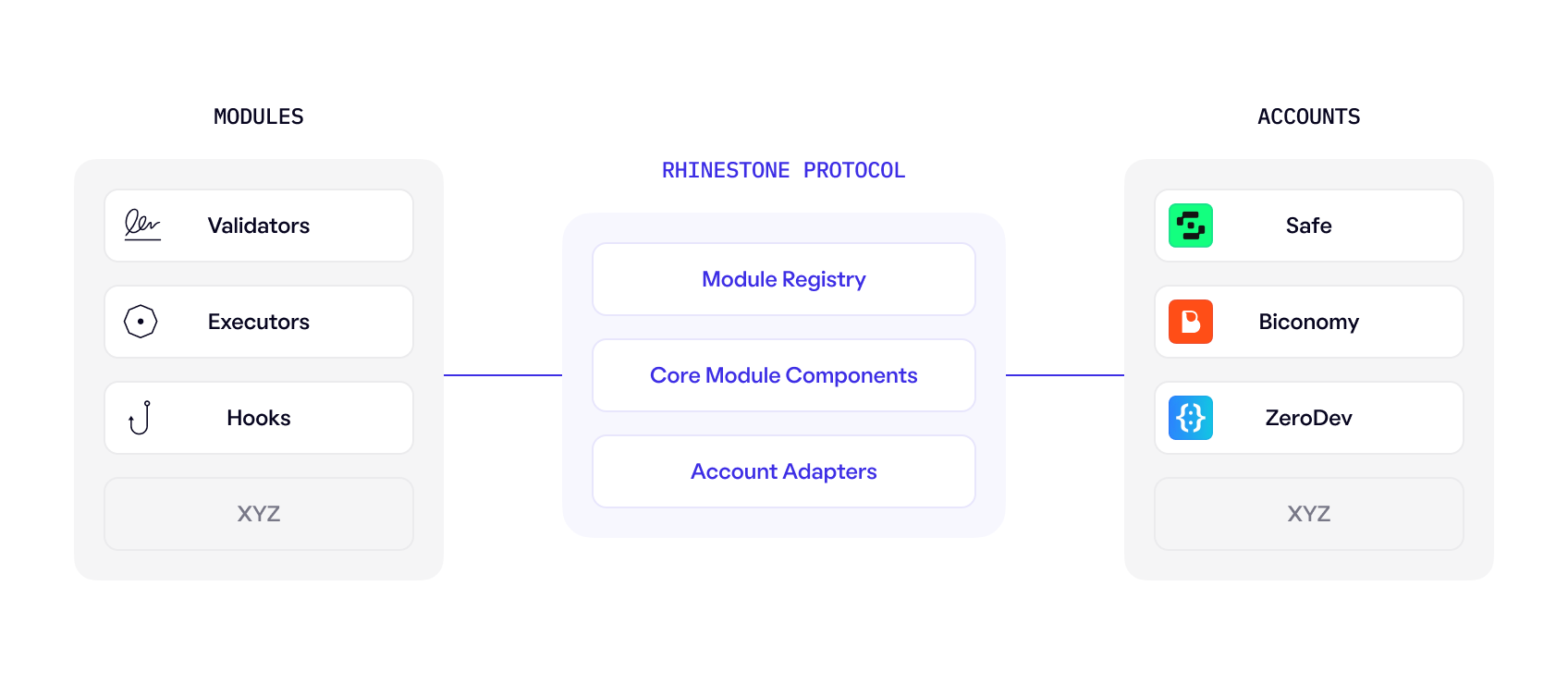
Components
- Modules: Smart contracts that extend the features of smart accounts.
- Accounts: Different smart account implementations built and integrated by trusted account vendor partners.
- Module Registry: The foundational layer of the Rhinestone Protocol. Its primary function is to enforce standards and security guarantees for users and developers by storing onchain security assertions made by independent auditors.
- Core Module Components: Complex module functions that are required across many different types of modules (for example, module monetization enforcement). These components are optionally inherited by the developer.
- Account Adapters: A communication layer that exists between different account implementations and the Module Registry. Adapters allow users, application developers, and/or account vendors to configure their security postures and ensure modules meet a predefined set of security rules and guidelines.